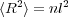
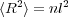 | (4) |
We may represent an ideal polymer chain which for which we account for local interactions via C∞ etc. by an equivalent freely jointed chain. The equivalent chain has the same fully extended length of the actual chain, Rmax, and the same mean square end-end distance. It is composed of N subunits of length b such that Nb = Rmax and < R2 >= Nb2 = C∞nl2, so that