
For example, in elongation of a polymer chain due to tension, we may assume these blobs are more or less lined-up along the direction of deformation. The number of blobs is (N∕g) so that the extension R ≈ ξ (N∕g). From this, we see that

The free energy of the chain is increased in tension due to the restriction of the degrees of freedom of the blobs - each blob in this case contributes kT and so
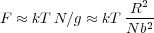
If we consider the force required to stretch the polymer coil
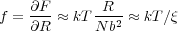 | (9) |
we see that the blob defines a length scale over which the elastic energy is ≈ kT. That is, under an external force, the polymer will be unperturbed on length scales smaller that that for which the corresponding ‘thermal forces’ are kT or larger.