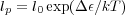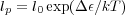1.1 Static Flexibility
The static flexibility of the chain in equilibrium is determined by the difference between the levels of the energy
minima corresponding the gauche and trans states, Δε.
-
- If Δε < kT, the g+, g- and t states occur with similar probability, and so the chain can change direction
and appears as a random coil.
-
- If Δε takes on a larger value, then the t conformations will be enriched, so the chain will be rigid locally,
but on larger length scales, the eventual occurrence of g+ and g- conformations imparts a random
conformation.
-
- Overall, if we ignore details on some length scale smaller than lp, the persistence length, the polymer appears
as a continuous flexible chain where
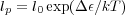 | (1) |
where l0 is something like a monomer length.